Colorado
The Regional Imaging teams in Colorado are lucky to have two effective sponsors: Joseph Gonzales, clinical operations for Regional Imaging, and Rebecca “Becky” Torres, a pharmacy technician and SEIU Local 105 member. Part of their success, the pair says, is the emphasis they have placed on sharing information—with each other and with their teams. The pair also figured out a way to spread effective practices. Using a PowerPoint template, the sponsors asked co-leads to explain what they’re working on, how it supports regional goals, whether it worked and the outcome. Then, the teams came together for a UBT Fair and shared their PowerPoints.
Georgia
David Jones, MD, has a title unique at Kaiser Permanente: assistant to the medical director for unit-based teams. He mobilizes his fellow physicians in the Georgia region to get involved with UBTs and unleash the power of partnership to improve performance and grow membership. “The first thing I tell physicians about the UBTs is that it is about improving the work that we’re already doing,” he says. “It’s not about adding more work, it’s about looking at the work you're doing and figuring out how to do it better.” Read more from Jones—including how his experience with UBTs has transformed the way he delivers care to his patients.
Hawaii
A small region, Hawaii needed a novel approach to sponsorship: Branch out rather than always branch up. Initially, a five-member unit-based team committee tried to troubleshoot issues for the region’s fledgling teams. Often, those committee members, who also had roles as team co-leads or contract specialists, were trying to wear too many hats and got jammed. So the region, which now has more than 40 teams, has tapped 19 people to receive sponsorship training. The group includes middle managers, directors and other executives, frontline nurses who serve on the Kaiser Permanente board of the Hawaii Nurses Association, OPEIU Local 50, and former labor team members and co-leads.
Mid-Atlantic States
While the Mid-Atlantic States region’s clinical unit-based teams have management and labor co-sponsors, large teams such as lab and radiology are sponsored in a different way: A UBT leadership group made up of labor and management from these area performs sponsorship functions as a united body. “We generated a vision of our UBT sponsorship. We got very specific on how we would work together,” says Jane Lewis, executive director of health plan regional services and a member of the group that sponsors eight pharmacy UBTs. The UBTs report their projects and team dynamics at monthly meetings. The leadership group reviews People Pulse, service scores, quality results and other metrics, identifies struggling teams, and recognizes teams that excel.
Northern California
The region has been on a roll with its “A Leader’s Role as UBT Sponsor” training. Launched in the spring, the tutorial gives management and labor leaders an easy-to-understand yet in-depth look at providing effective support to unit-based teams and their performance improvement work. The short, online training covers everything from outlining a sponsor’s role and how a sponsor can model partnership to tips on developing strong UBT co-leads and high-performing teams. Several facilities have combined the training with in-person, interactive exercises, and early feedback suggests the blended approach is striking a chord with sponsors. The online training can be found at KP Learn.
Northwest
“My role as a senior sponsor is to bring the message of UBTs to physician leadership,” says Rasjad Lints, MD, the region’s executive sponsor of UBTs. Lints is especially interested in helping teams focus on outcome metrics—a measure of the final result of something, such as how many patients with hypertension have their blood pressure under control—and to help everyone on the team understand that improving on process metrics often drives improvement on outcomes. It can be difficult to see the value in participating in process metrics if team members don’t see how it relates to the outcome measures. “At the end of the day, physicians have to drive the care,” Lints says. While working in UBTs presents physicians with some unique challenges, he believes that “if the physicians aren’t engaged, it’s a lost opportunity.”
Ohio
In an effort to improve the quality of team project information in UBT Tracker, the regional LMP support team solicited the help of the people who support the work of teams—sponsors. In June, an improvement adviser met with Ohio’s 20-plus sponsors and asked them to work with their teams to boost the input of that data. To illustrate the value and role of quality data in UBT Tracker, they used the data in Tracker to brief the sponsors on their UBTs’ projects and status. Their approach made an impact: The region has reported an increase in sponsor engagement, and several teams have reported performance and relationship improvements.
Southern California
The regional Labor Management Partnership department is launching a new sponsor training curriculum that covers the nuts and bolts of what sponsors do and how they do it. Topics include: the responsibilities of sponsoring bodies (such as helping define how the teams should be structured and guiding selection of co-leads); coaching skills to help develop UBT leaders; the similarities and differences between labor and management sponsorship; how managing in partnership differs from traditional management; and how the sponsor role differs from that of facilitators, project managers, trainers and consultants. Also included in the course are basics of the Labor Management Partnership and unit-based teams, such as the key elements for UBT success, the roles and responsibilities of UBT co-leads and members, and consensus decision making.


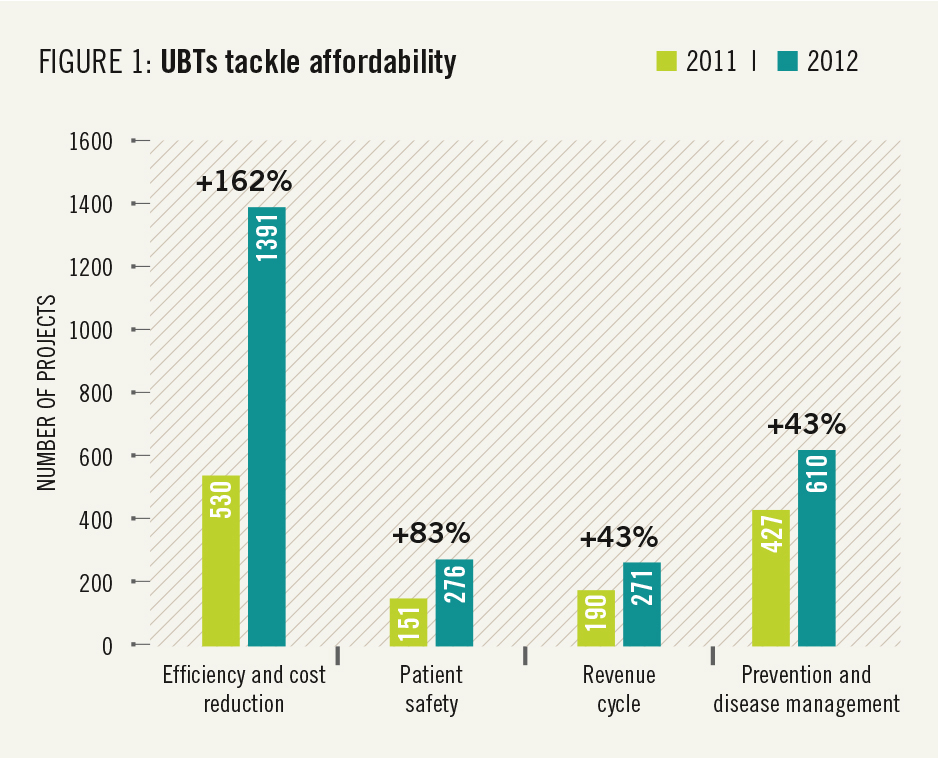 This report highlights many ways that unit-based teams are getting results that matter to members and patients. Affordability of care, one of the issues that matters most to members, was the fastest-growing focus area for UBTs in 2012 (see Figure 1).
This report highlights many ways that unit-based teams are getting results that matter to members and patients. Affordability of care, one of the issues that matters most to members, was the fastest-growing focus area for UBTs in 2012 (see Figure 1). And these teams are getting results. Waste- and cost-reduction projects can yield immediate savings of $20,000 to $50,000. Spread across the organizations, these efforts could save more than $100 milliion a year. Some examples of the work being done:
And these teams are getting results. Waste- and cost-reduction projects can yield immediate savings of $20,000 to $50,000. Spread across the organizations, these efforts could save more than $100 milliion a year. Some examples of the work being done: But those changes are coming. “The growing number of cost saving and efficiency projects are helping build a culture of savings and waste reduction among high-performing teams across KP,” says Peter Nixon, director of metrics and analytics, Office of Labor Management Partnership.
But those changes are coming. “The growing number of cost saving and efficiency projects are helping build a culture of savings and waste reduction among high-performing teams across KP,” says Peter Nixon, director of metrics and analytics, Office of Labor Management Partnership.