Do teams get better results when frontline workers are engaged, free to speak and can influence decisions? Yes, say the people who know best — Kaiser Permanente workers and managers themselves.
Recent People Pulse surveys confirm that unit-based teams get positive results for health plan members and patients, the organization and workers themselves.
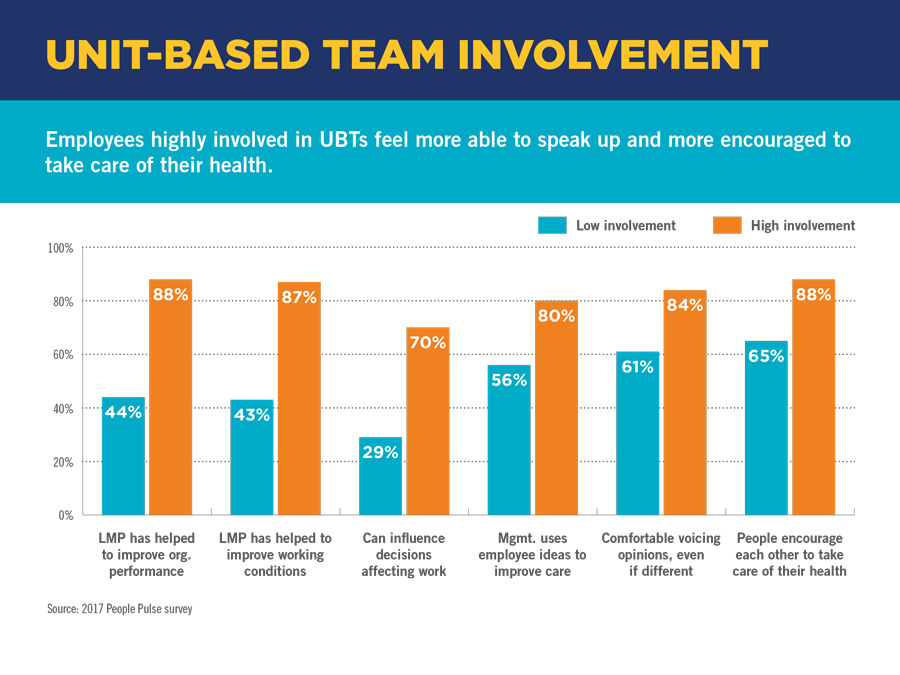
For instance, the 2017 People Pulse survey of more than 155,000 KP employees showed that when union-represented employees are highly involved in UBT activities, they get 29 percent higher scores on measures of their willingness to speak up — a key driver of patient and workplace safety and satisfaction. They also get 33 percent higher scores on questions regarding workplace health and wellness.
Improved safety and satisfaction
Further analysis, included in the 2016 People Pulse survey, showed that teams with high employee involvement have:
- 18 percent fewer workplace injuries
- 13 percent fewer lost work days
- 4 percent higher patient satisfaction
“Our findings show that employees who are highly involved in their unit-based teams feel more able to speak up and more encouraged to take care of their health,” says Nicole VanderHorst, principal research consultant with KP Engagement & Inclusion Analytics. “That makes them more likely to have better performance outcomes.”
A better way to work
Workers’ greater propensity to speak up and look after their health when they’re involved in team activities covers several questions (see chart below). For example, workers who are highly involved in their UBTs are far more likely to say:
- The Labor Management Partnership has helped improve organizational performance and working conditions.
- They can influence decisions affecting their work.
- They’re comfortable voicing differing opinions.
- Management uses their ideas to improve care.
- They’re encouraged, and encourage others, to take care of their health.
Click to enlarge.
Roots of workforce engagement
All these factors contribute to a better employee experience as well as performance. And UBTs reflect KP’s unique history with the labor movement.
“Henry Kaiser was perhaps the 20th century’s most worker-friendly industrialist. He supported organized labor and knew that people step up when allowed to exert their job experience, as they do with UBTs,” says KP archivist and historian Lincoln Cushing. “He trusted employees to make decisions that benefitted themselves and their organizations.”
If you belong to a unit-based team — and most union-represented employees do — talk with a team co-lead about ways to get more involved.